Healthcare covers a broad range of diseases and disorders that can harm our health. Infectious diseases come from outside organisms like bacteria and viruses. These can spread from person to person, by insects, or through food and water. Signs that you might have one include fever, tiredness, and coughing. But, lots of infectious diseases can be avoided with vaccines and keeping your hands clean.
Then, there are non-infectious diseases which we don’t catch from others, but come from our genes, age, or what’s around us. Some big ones are cancer, diabetes, and Alzheimer’s. The cause and how they make us feel can vary a lot. These diseases all need the right treatment and care for people to get better.
Some people are more likely to get infectious diseases, like cancer patients or those with HIV. So are young kids, pregnant women, and the elderly. People who are not vaccinated and healthcare workers also face more risk. Going to places with a lot of transmissible diseases, like mosquito sicknesses, can make you more likely to get sick.
Serious cases of infectious diseases can lead to big health problems. These can include dehydration, pneumonia, sepsis, and meningitis. Knowing how these diseases work, what to look out for, and how to avoid them is key to staying healthy.
Key Takeaways
- Infectious diseases are caused by organisms like bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites.
- Common symptoms of infectious diseases include fever, fatigue, coughing, and muscle aches.
- Many infectious diseases can be prevented through vaccination and proper hygiene practices.
- Certain populations, such as those with weakened immune systems and healthcare workers, are at higher risk for infectious diseases.
- Complications from infectious diseases can be severe, including dehydration, pneumonia, sepsis, and meningitis.
Understanding Infectious Diseases
Infectious diseases are caused by harmful pathogens, including viruses, bacteria, fungi, and parasites. These can cause a variety of illnesses, from colds to serious diseases like AIDS and tuberculosis. Knowing about these diseases helps us prevent and treat them.
Viral Infections
Viral infections come from viruses, small genetic pieces in a protective layer. Illnesses like the flu, measles, HIV, and COVID-19 are viral. They are a big concern because viruses easily spread from person to person.
Bacterial Infections
Bacterial infections are from single-cell organisms. They can release toxins and cause diseases like strep throat and tuberculosis. Bacteria spread through direct contact, food, water, and other ways, making them common.
Fungal Infections
Fungal infections happen when harmful fungi overgrow on the body. Illnesses like ringworm and yeast infections fall into this category. They are especially hard to treat for those with weak immune systems.
Parasitic Infections
Parasites use other organisms to live, causing diseases such as malaria. These can come from insect bites, dirty food, water, and more. It’s a big concern worldwide.
Apart from these, there’s a rare set of illnesses called transmissible spongiform encephalopathies (TSEs) or prion diseases. They’re caused by bad proteins. Knowing about all these diseases and how they spread is key to stopping them.
Common Symptoms of Infectious Diseases
Infectious diseases usually show certain common symptoms. The main signs are fever, fatigue, coughing, and muscle aches. These show the body is likely trying to fight an infection from viruses, bacteria, fungi, or parasites.
Fever
Fever is a key symptom for many infectious diseases. The body increases its temperature to make a hostile place for the harmful invaders. This is an important way the immune system tries to fight off infections.
Fatigue
Infectious illnesses often lead to feeling very tired. The body uses a lot of energy to fight the infection. So, it’s common to feel an overwhelming lack of energy when you’re sick.
Coughing
Illnesses that affect the lungs, like the flu or pneumonia, can cause a lot of coughing. Coughing helps the body clear out the infection from the lungs and airways.
Muscle Aches
Feeling sore or achy all over is also common with infectious diseases. This can be from the body’s fight against the illness or the direct impact the infection has on muscles.
Symptoms may vary by the kind of disease, but fever, fatigue, coughing, and muscle aches often mean an infection fight is happening. Knowing these signs can help get early medical help and the right treatment.
Transmission and Causes
Infectious diseases spread in various ways, like through direct touch, coughing, or touching objects. Direct contact happens with touch or air from someone sick. Indirect contact is when you pick up germs from objects. Mosquitoes and ticks can spread disease too, through their bites.
Food and water contamination is also a biggie.
This allows sickness to quickly move from one person to many, like in E. coli outbreaks. Knowing how these diseases spread helps us stop them.
Direct Contact
If you touch infected people or animals, you might pick up a sickness. This includes things like shaking hands or getting coughed on.
Even sexual contact or bites and scratches from animals can spread disease.
Indirect Contact
Indirect contact means you can get sick from touching contaminated objects. Things like doorknobs or shared items can be hot spots for germs.
This allows diseases to move without directly interacting with an infected person.
Insect Bites
Insect vectors play a big role in spreading sickness. Mosquitoes, fleas, lice, and ticks can all pass diseases to us through their bites.
For instance, mosquitoes can carry the malaria parasite and infect humans.
Food Contamination
Food and water contamination is a common cause of widespread illnesses. If food is undercooked or water is dirty, it can carry bacteria like E. coli and Salmonella. This is why it’s crucial to prepare food safely and ensure water sources are clean.
Risk Factors for Infectious Diseases
Some people are more likely to get infectious diseases. These include those with a weakened immune system. People with cancer or HIV are at higher risk. Young children, pregnant women, and older adults also face more danger.
Unvaccinated people are at risk too. Also, those who work in healthcare. They may come into contact with diseases often. Going to places where diseases like malaria and dengue are common can also make you more open to getting sick.
It’s really important to know these risk factors. This knowledge can help you avoid getting sick. By focusing on the most vulnerable groups, we can help them and protect ourselves too.
| Risk Factor | Description |
|---|---|
| Weakened Immune System | Conditions like cancer, HIV/AIDS, and other immune system disorders can increase susceptibility to infectious diseases. |
| Age | Young children and older adults are more vulnerable to infectious diseases due to their developing or weakening immune systems. |
| Lack of Vaccination | Unvaccinated individuals are at a higher risk of contracting common infectious diseases that can be prevented through immunization. |
| Healthcare Workers | Frequent exposure to infectious patients and environments puts healthcare workers at an elevated risk of contracting infectious diseases. |
| Travel | Visiting regions with highly transmissible diseases, such as mosquito-borne illnesses, can increase the chances of infection for travelers. |

Complications of Infectious Diseases
Many infectious diseases get better on their own. But, some can be very serious. They might even be life-threatening. For example, dehydration can happen if you have a fever, are vomiting, or have diarrhea. This is often seen with infectious disease infections.
Pneumonia, which is an inflamed lung, can happen after getting a respiratory infection like the flu or COVID-19. Sepsis is a severe body response to infections. It is very dangerous and sometimes deadly. Meningitis can also occur. It causes the area around the brain and spinal cord to swell. This can come from viral, bacterial, fungal, or parasitic infections.
Dehydration
Dehydration is common in infectious diseases. Especially ones that come with a fever or cause vomiting and diarrhea. It’s crucial to treat dehydration. If left untreated, it can cause serious health problems.
Pneumonia
Pneumonia is an infection in the lungs. It often comes from respiratory infections. It can make it hard to breathe. People might need to go to the hospital. In severe cases, it can lead to death.
Sepsis
Sepsis is when the body’s immune system reacts too much to an infection. It causes serious inflammation and can make your organs fail. Bacterial infections are most often the cause.
Meningitis
Meningitis causes the area around the brain and spinal cord to swell. It can cause problems with the nerves, long-term disabilities, and sometimes death. It’s usually caused by viruses or bacteria.
It’s very important to treat infectious diseases promptly. This helps avoid the serious and sometimes deadly complications they can cause.
Common Diseases and Disorders: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatments
In addition to infectious diseases, many other common diseases and disorders can affect people. These include noninfectious issues, such as asthma, autism, autoimmune diseases, breast cancer, and obesity. The causes and symptoms of these conditions can be different. Yet, they all need medical attention and the right treatments.
Medical care may include medicines, therapies, changes in how you live, and sometimes surgery. It’s important to know the signs of these conditions and what can help. This knowledge is key for preventing, diagnosing, and treating these health issues effectively.
Asthma
Asthma is a chronic lung disease that makes it hard to breathe. It often causes wheezing, coughing, and chest tightness. These symptoms happen because the airways in the lungs become narrow and inflamed.
Around 25 million Americans have asthma. Every year, it leads to 1.6 million ER visits in the U.S. These attacks can be mild or severe, and they vary from person to person.
There are many types of asthma, like adult-onset asthma or asthma in kids. Allergic asthma, triggered by allergens like pollen, is common. Others include exercise-induced asthma and asthma caused by stress.
The likelihood of asthma also goes up with family history and certain environmental factors. Race, gender, and job also play a role. While asthma can’t be cured, the right treatments can help control its symptoms.
| Asthma Statistics | Value |
|---|---|
| Americans affected by asthma | 25 million |
| Annual emergency room visits for asthma | 1.6 million |
| Estimated people affected by asthma globally in 2019 | 262 million |
| Asthma-related deaths globally in 2019 | 455,000 |
Symptoms of asthma can be different among people. Some may not have attacks very often, but for others, symptoms are constant.
Asthma can be hard for daily life. Regular treatment is important to prevent severe problems. This can include ER visits or being hospitalized.
Key to managing asthma is knowing your symptoms and triggers. Use a peak flow meter to track your breathing. Taking medicines as directed is essential.
Autism Spectrum Disorder
Autism, also known as autism spectrum disorder, is a group of conditions that change how people talk and act. Signs usually show up by age 2. It’s a difference in the brain that affects thoughts and the way we understand the world. The CDC says autism affects 1 in 36 kids in the U.S.
The DSM-5 lists trouble with talking and making friends, fixed interests, and doing things repetitively as things seen in those with autism. It’s called a spectrum because it includes a variety of symptoms and effects. This can mean from mild to severe differences in life.
About 1 in every 44 kids in the U.S. has autism by age 8. It’s more common in boys by over four times. The reason for this large difference isn’t fully clear.
Possible signs of autism, like changes in behavior, often show between 1.5 and 3 years of age. Boys are more likely to be diagnosed than girls. The number of autism cases is going up. This is possibly because we’re getting better at spotting it, more people actually have it, or both.
Anyone can have autism, no matter their gender, race, or family’s wealth. Experts say it’s important for all kids to be checked for autism early. This can help them get the right support soon.
Kids get looked over for signs of autism at 18 and 24 months. Those who might seem different at these checks might need extra tests. This can include seeing different doctors who work together to understand a child’s needs.
Older kids, teens, and grown-ups need special attention to spot autism. Teachers, family, and other caregivers can help share what they’ve seen. Getting a right diagnosis as an adult might clear up past struggles and show how to get help.
Studies are looking at how best to help young adults with autism fit into society better. Having one child with autism raises the chance you might have another with it. Autism can sometimes be linked to health problems like fragile X syndrome or Rett syndrome.
Autoimmune Diseases
Autoimmune diseases happen when our immune system gets confused. It attacks the body’s healthy cells, tissues, and organs. This can make our body weaker and sometimes leads to dangerous outcomes. Inflammation is good in fighting off illness. But too much in certain diseases hurts the body.
Females born between 15 and 44 have a higher chance of getting autoimmune diseases than males. Some groups are more affected, like White people in Europe and the U.S. see more muscle diseases. In contrast, lupus is common among African American, Hispanic, or Latino groups.
More than 24 million Americans have an autoimmune disease. Doctors know over 100 kinds. Common ones include type 1 diabetes, MS, RA, lupus, Crohn’s, and psoriasis. Surprisingly, 78% of those with these diseases are women.
Inflammation
Chronic inflammation is linked to many autoimmune diseases. It damages our body. The immune system mistakenly attacks our healthy cells, tissues, and organs. Learning to manage this inflammation is crucial in treating these conditions.
Smoking, toxins, being female, and obese can raise your risk for autoimmune disorders. Some autoimmune diseases can be passed in families due to genes. Knowing these risks can help prevent or manage the diseases.
Diagnosing autoimmune diseases isn’t easy. The symptoms look like many other illnesses. It might take time to get the right diagnosis, with several blood tests needed, like ANA and CBC.
While there’s no cure currently, treatments focus on controlling the immune system and symptoms. Research keeps looking for better therapies. This offers hope for those with autoimmune diseases.
Breast Cancer
Breast cancer ranks second among cancers found in US women. About 1 in 8 women get diagnosed each year, and most don’t have a family history of it. This hints that things in our environment might cause breast cancer. Early detection is key, since breast cancer is the second cause of death in women, next to lung cancer.
Men can get breast cancer too, though less than 1% of cases are in men. The chance of getting breast cancer goes up with age. Over 55% of women with breast cancer are 55 or older. White women get breast cancer more often than other races. Black women have a higher risk of getting it before menopause.
Several things can raise the risk of breast cancer. These include early menstruation, late menopause, dense breast tissue, and regularly drinking alcohol. Other factors are having your first child after 30, never being pregnant, getting older, being obese, and certain genetic mutations. What’s surprising is that 75% of women with breast cancer have none of these risk factors.
Survival from breast cancer is getting better. Also, fewer people are dying from it now. This good news is thanks to better ways to find and treat the cancer. Plus, there’s a lot of work to spread the word about it. Knowing the risks, supporting regular checks, and choosing a healthy lifestyle all help in the fight against breast cancer.
Kidney Disease
An epidemic of chronic kidney disease is spreading, yet its causes are not fully known. This condition, CKDu, means your kidneys lose function over time and can be deadly. It mainly affects people working in agriculture in hot and humid places, hinting at environmental causes.
One in seven American adults has chronic kidney disease, mainly due to diabetes. If this disease progresses, up to 90% of kidney function can be lost. This is when end-stage kidney failure happens, requiring either dialysis or a kidney transplant to stay alive.
There are steps to manage kidney disease. For instance, quitting smoking, limiting alcohol, and keeping a healthy weight. Being active and finding support from friends or groups can also make a big difference. These actions can slow down the disease and improve someone’s health.
Around 1 in every 7 US adults has chronic kidney disease, yet up to 40% don’t know it. Diabetes and high blood pressure are top reasons for this illness. People from certain backgrounds, like Black or Latino people, might face a higher risk due to a specific gene problem.
To tackle this issue, like the spread of CKDu among agricultural workers in hot spots, we need a big plan. This includes looking at the environment, finding cases early, and having good ways to manage the disease. Such an effort could help many people.
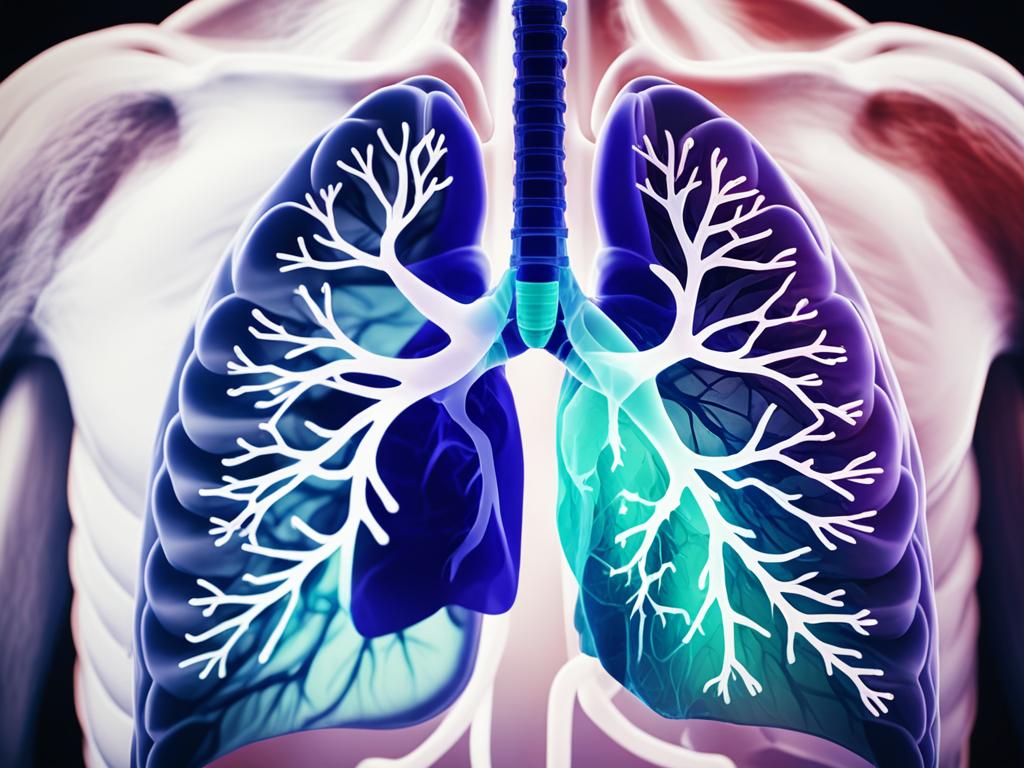
Lung Diseases
Lung disease is a group of issues that stop the lungs from working well. It makes it hard to breathe and affects how our lungs work. This group includes many illnesses, from asthma to serious ones like lung cancer and COPD.
In the U.S., millions of people have lung diseases. The top causes are smoking, infections, and our genes. Asthma, which causes constant airway inflammation, affects many people. COPD makes it hard to breathe for many others. Pneumonia is a common lung infection due to bacteria or viruses like COVID-19, worsening breathing issues.
Emphysema harms the alveoli and reduces air flow, often due to smoking. Lung cancer targets the main lung area near the air sacs. Severe illnesses such as COVID-19 can lead to ARDS, needing ventilators for many. Pneumoconiosis, from inhaling harmful stuff, includes black lung disease and asbestosis.
There’s also pulmonary embolism, pulmonary hypertension, mesothelioma, and more. They can cause breathing and lung problems. This leads to chest pain, trouble breathing, and feeling short of breath. In Canada, many people face chronic coughs, and COPD often lands people in the hospital. This shows how lung diseases affect many.
Obesity
Obesity is considered a major health issue, affecting over 30% of adults and 17% of U.S. kids and teens. It’s not just about eating too much and moving too little. Many things contribute, like our genes, how our bodies work, and the world around us. We often end up taking in more calories than we burn, leading to weight gain. This is made worse by not having easy access to healthy foods, lack of chance to exercise, and serving sizes that are too big.
Our genes and what our bodies do with food are key too. Health issues like an underactive thyroid and certain meds can make it easier to gain weight. We might also inherit a tendency for obesity from our families. This could be because of how our bodies store fat, use energy, and handle hunger. How well we burn calories while we move also plays a role.
The world we live in also makes a big difference. If it’s hard to find affordable, healthy food or places to be active, it’s tough to stay healthy. Stress and not getting enough sleep can also lead to being overweight or obese. We now know that being too heavy increases the risk of many serious health problems. These include heart diseases, diabetes, and certain cancers. Dealing with obesity is a big challenge for public health.
Source Links
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/infectious-diseases/symptoms-causes/syc-20351173
- https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/17724-infectious-diseases
- https://www.healthline.com/health/autoimmune-disorders
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/infectious-diseases/diagnosis-treatment/drc-20351179
- https://healthcare.utah.edu/infectious-diseases/general
- https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/communicable-diseases
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7150340/
- https://www.webmd.com/asthma/what-is-asthma
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/asthma/symptoms-causes/syc-20369653
- https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/asthma
- https://www.nimh.nih.gov/health/topics/autism-spectrum-disorders-asd
- https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/8855-autism
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/autism-spectrum-disorder/symptoms-causes/syc-20352928
- https://www.webmd.com/a-to-z-guides/autoimmune-diseases
- https://www.webmd.com/breast-cancer/understanding-breast-cancer-basics
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/breast-cancer/symptoms-causes/syc-20352470
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/breast-cancer/diagnosis-treatment/drc-20352475
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/chronic-kidney-disease/symptoms-causes/syc-20354521
- https://www.webmd.com/a-to-z-guides/understanding-kidney-disease-basic-information
- https://www.kidney.org/atoz/content/about-chronic-kidney-disease
- https://www.webmd.com/lung/lung-diseases-overview
- https://www.lung.ca/lung-health/lung-diseases
- https://www.nichd.nih.gov/health/topics/obesity/conditioninfo/cause
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/obesity/symptoms-causes/syc-20375742


